|
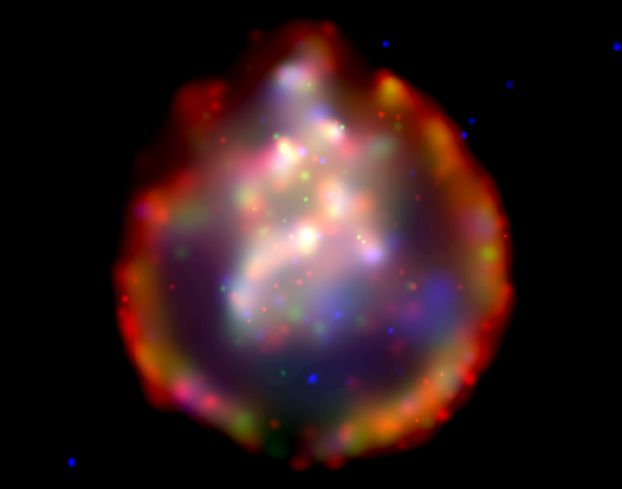
Explanation: A supernova explosion, a massive star's inevitable and spectacular demise, blasts back into space debris enriched in the heavy elements forged in its stellar core. Incorporated into future stars and planets, these are the elements ultimately necessary for life. Seen here in a false-color x-ray image, supernova remnant SNR 0103-72.6 is revealed to be just such an expanding debris cloud in neighboring galaxy, the Small Magellanic Cloud. Judging from the measured size of the expanding outer ring of shock-heated gas, about 150 light-years, light from the original supernova explosion would have first reached Earth about 10,000 years ago. Hundreds of supernova remnants have been identified as much sought after astronomical laboratories for studying the cycle of element synthesis and enrichment, but the x-ray data also show that the hot gas at the center of this particular supernova remnant is exceptionally rich in neon and oxygen.
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Based on Astronomy Picture
Of the Day
Publications with keywords: supernova - supernova remnant - nucleosynthesis - SMC
Publications with words: supernova - supernova remnant - nucleosynthesis - SMC
See also:
- APOD: 2025 October 1 Á NGC 6960: The Witchs Broom Nebula
- APOD: 2025 July 31 Á Supernova 2025rbs in NGC 7331
- APOD: 2025 June 9 Á Between Scylla and Charybdis: A Double Cosmic Discovery
- Supernova Remnant Cassiopeia A
- APOD: 2025 January 8 Á Supernova Remnants Big and Small
- APOD: 2024 September 18 Á The Mermaid Nebula Supernova Remnant
- APOD: 2024 April 16 Á Filaments of the Vela Supernova Remnant