|
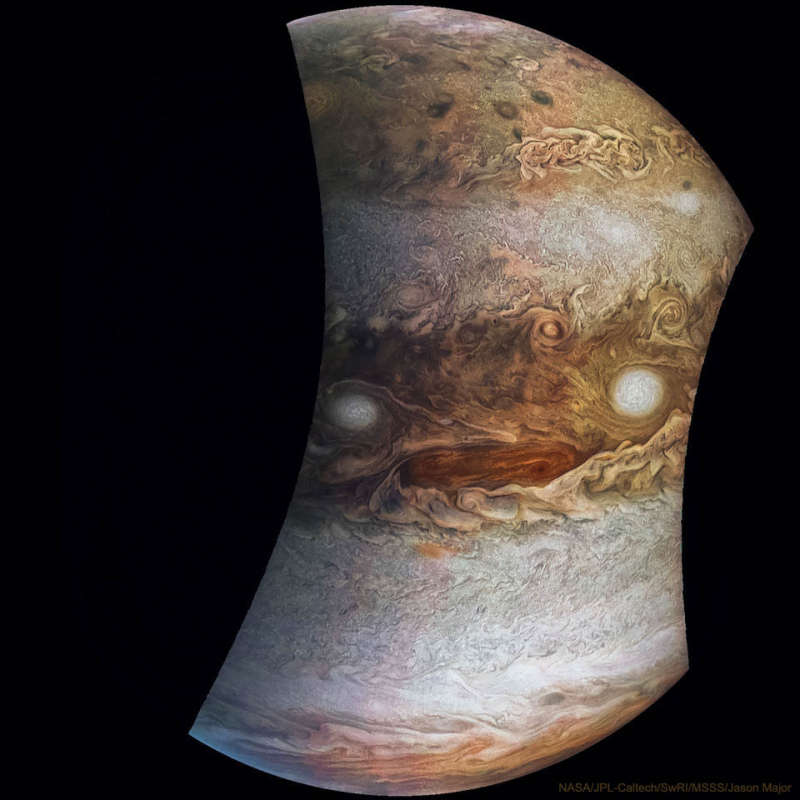
Explanation: What do you see in the clouds of Jupiter? On the largest scale, circling the planet, Jupiter has alternating light zones and reddish-brown belts. Rising zone gas, mostly hydrogen and helium, usually swirls around regions of high pressure. Conversely, falling belt gas usually whirls around regions of low pressure, like cyclones and hurricanes on Earth. Belt storms can form into large and long-lasting white ovals and elongated red spots. NASA's robotic Juno spacecraft captured most of these cloud features in 2017 during perijove 6, its sixth pass over the giant planet in its looping 2-month orbit. But it is surely not these clouds themselves that draws your attention to the displayed image, but rather their arrangement. The face that stands out, nicknamed Jovey McJupiterFace, lasted perhaps a few weeks before the neighboring storm clouds rotated away. Juno has now completed 33 orbits around Jupiter and just yesterday made a close pass near Ganymede, our Solar System's largest moon.
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Based on Astronomy Picture
Of the Day
Publications with keywords: Jupiter
Publications with words: Jupiter
See also:
- APOD: 2026 January 6 Á Jupiters Clouds in High Definition from Juno
- APOD: 2025 November 11 Á Jupiter in Ultraviolet from Hubble
- APOD: 2025 December 14 Á Juno Flyby of Ganymede and Jupiter
- APOD: 2025 May 25 Á Beneath Jupiter
- Painting with Jupiter
- APOD: 2025 April 2 Á Jupiter and Ring in Infrared from Webb
- APOD: 2025 March 9 Á Cyclones at Jupiters North Pole