|
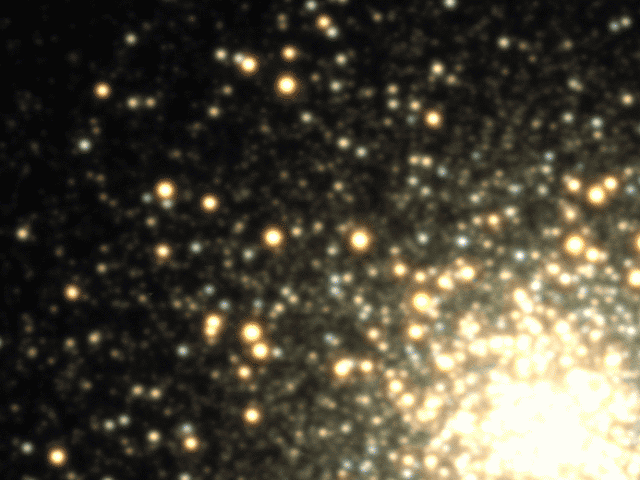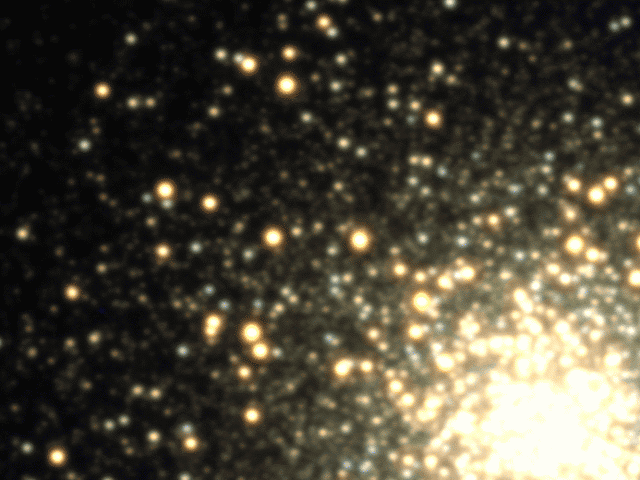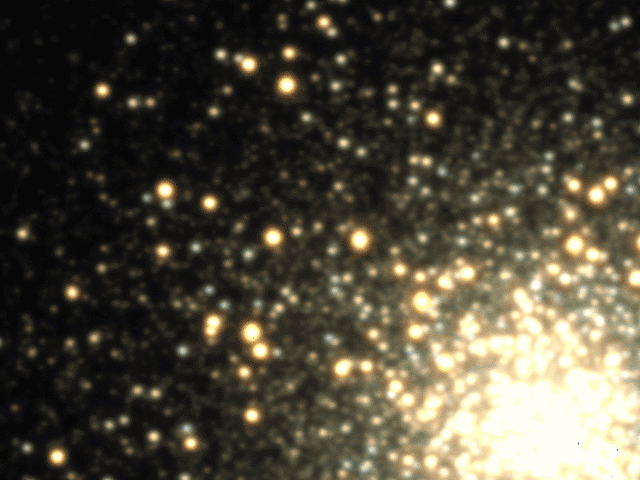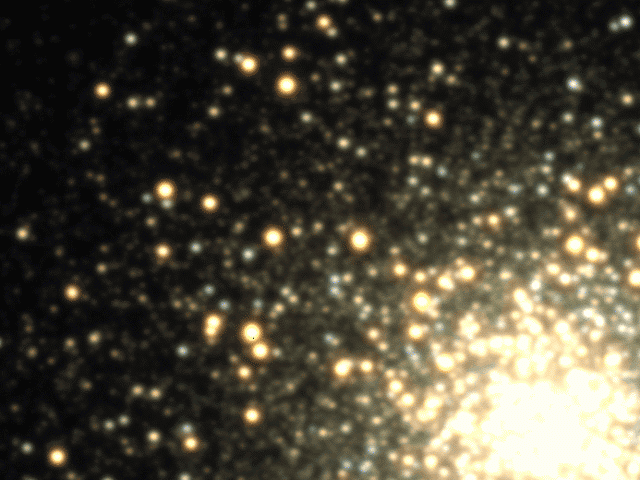
Explanation: Star clusters appear constant because photographs of them are frozen in time. In reality, though, cluster stars swarm the center and frequently fluctuate in brightness. Although the time it takes for stars to cross a cluster is about 100,000 years, the time it takes for a star to fluctuate noticeably can be less than one night. In fact, the above time lapse movie of bright globular cluster M3 was taken over a single night. Most of the variable stars visible above are RR Lyrae stars, stars that can quickly double their brightness while becoming noticeably bluer. Furthermore, RR Lyrae stars vary their light in a distinctive pattern that allows unique identification. Lastly, since RR Lyrae stars all have the same intrinsic brightness, identifying them and measuring how dim they appear tells how far they are, since faintness means farness. These distances, in turn, help calibrate the scale of the entire universe.
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings, and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris. Specific rights apply.
A service of: LHEA at NASA / GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Based on Astronomy Picture
Of the Day
Publications with keywords: M 3 - globular cluster
Publications with words: M 3 - globular cluster
See also:
- APOD: 2025 December 28 Á NGC 1898: Globular Cluster in the Large Magellanic Cloud
- APOD: 2025 November 26 Á Globular Cluster M15 Deep Field
- APOD: 2025 September 5 Á 47 Tucanae: Globular Star Cluster
- APOD: 2025 August 14 Á M13: The Great Globular Cluster in Hercules
- APOD: 2025 July 26 Á Globular Cluster Omega Centauri
- NGC6366 vs 47 Ophiuchi
- Messier 2