
|
Astronomy Picture Of the Day (APOD)
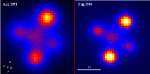 Microlensing of the Einstein Cross
Microlensing of the Einstein Cross
11.07.1995
The famous "Einstein Cross" is a case where a single object is seen four times. Here a very distant QSO happened to be placed right behind a massive galaxy. The gravitational effect...
 Abell 2218: A Galaxy Cluster Lens
Abell 2218: A Galaxy Cluster Lens
10.07.1995
Sometimes one of the largest concentrations of mass known can act like a lens. Almost all of the bright objects in this image are galaxies in the cluster known as Abell 2218. The cluster...
 A Meteoric View of Apollo 13
A Meteoric View of Apollo 13
9.07.1995
Meteors, also called shooting stars, normally begin as bits of dust from the tails of comets or even small pieces chipped off asteroids. Falling toward Earth, these particles enter the atmosphere at extremely high speeds. Friction with the air heats them up and makes them glow brightly.
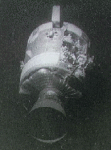 Damage to Apollo 13
Damage to Apollo 13
8.07.1995
In April of 1970, after an oxygen tank exploded and damaged their service module, the Apollo 13 astronauts were forced to abandon their plans to make the third manned lunar landing. The extent...
 Lunar Farside from Apollo 13
Lunar Farside from Apollo 13
7.07.1995
In April of 1970, after an explosion damaged their spacecraft, the Apollo 13 astronauts were forced to abandon their plans to make the third manned lunar landing. Still, while coasting around the moon in their desperate attempt to return to earth they were able to photograph the moon's far side.
 Saturn, Rings, and Two Moons
Saturn, Rings, and Two Moons
6.07.1995
This image of Saturn was made by NASA's robot spacecraft Voyager 2 as it began to explore the Saturn system in 1981. Saturn's famous rings are visible along with two of its moons, Rhea and Dione which appear as faint dots in the right and lower right part of the picture.
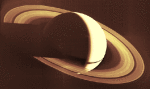 The Night Side of Saturn
The Night Side of Saturn
5.07.1995
This image of Saturn was made in November 1980 by the Voyager 1 spacecraft as it flew past the ringed gas giant planet. From a spectacular vantage point, looking back toward the inner solar system, the robot spacecraft recorded this view of the night side of Saturn casting a sharp shadow across the bright rings.
 The Firework Nebula
The Firework Nebula
4.07.1995
The Firework Nebula, known to astronomers as "GK Per", is the result of a type of stellar explosion called a nova. In a nova, a very compact star called a white dwarf blasts away gas that had accumulated on its surface.
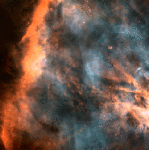 The Great Nebula in Orion
The Great Nebula in Orion
3.07.1995
The Great Nebula in Orion, M42, can be found on the night sky just below and to the left of the easily identifiable belt of three stars in the popular constellation Orion. This nebula is one of the closest stellar nurseries - where young stars are being formed even now.
 The Cartwheel Galaxy
The Cartwheel Galaxy
2.07.1995
The Cartwheel Galaxy shows a ring that is the result of a collision between a small and a large galaxy. After a small galaxy has moved through a big galaxy - in this case...
|
January February March April May June July August September October November December |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||