
|
Astronomy Picture Of the Day (APOD)
 Star Cluster in the Rosette Nebula
Star Cluster in the Rosette Nebula
22.05.1996
Embedded in the center of the colorful and photogenic Rosette Nebula is a bright, young open cluster. The bright blue stars in this cluster, labelled NGC 2244, emit ultraviolet light that knocks electrons away from hydrogen atoms.
 The Iron Sun
The Iron Sun
21.05.1996
The ultraviolet light emitted by eleven times ionized iron at temperatures over 2 million degrees Farenheit was used to record the above picture of the Sun on May 16. The image was made by the EIT camera onboard the SOHO spacecraft, a space observatory which can continuously observe the Sun.
 Helios Helium
Helios Helium
20.05.1996
Above is an image of the relatively quiet Sun made on May 18 in light emitted by ionized Helium atoms in the Solar chromosphere. Helium was first discovered in the Sun in 1868, its name fittingly derived from from the Greek word Helios, meaning Sun. Credit for the discovery goes to astronomer Joseph Lockyer.
 Nearby Dwarf Galaxy Leo I
Nearby Dwarf Galaxy Leo I
19.05.1996
Leo I is a dwarf spheroidal galaxy in the Local Group of galaxies dominated by our Milky Way Galaxy and M31. Leo I is thought to be the most distant of the eleven known small satellite galaxies orbiting our Milky Way Galaxy.
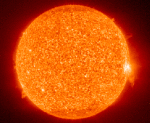
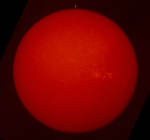 The Sun Today
The Sun Today
18.05.1996
Our Sun shows a different face every day. The above picture was taken on May 15, but a similar picture of the Sun actually taken today can be found here. The above picture was taken in red light and so is shown in red.
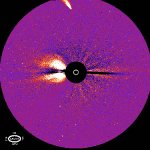 Comet Hyakutake and a Solar Flare
Comet Hyakutake and a Solar Flare
17.05.1996
A rare coincidence was recently captured by the orbiting SOHO spacecraft. During the closest approach to the Sun of Comet Hyakutake on May 1, SOHO photographed the comet. By accident -- during the time this photograph was being taken -- a solar flare was being ejected from the Sun.
 Comet Hyakutake Passes the Sun
Comet Hyakutake Passes the Sun
16.05.1996
On May 1, Comet Hyakutake made its closest approach to the Sun. During this time it was not possible to view the comet with most astronomical instruments because of the brightness of the nearby Sun.
 The Milky Way Near the Northern Cross
The Milky Way Near the Northern Cross
15.05.1996
This beautiful image of the sky near the bright star Deneb (just above center) reveals the stars, nebulae, and dark clouds along the plane of our Milky Way Galaxy as seen from the northern hemisphere (near Columbia Missouri, USA). Just below Deneb lies the suggestively shaped North American emission nebula.
 Hubble's Constant And The Expanding Universe (II)
Hubble's Constant And The Expanding Universe (II)
14.05.1996
In this century, the discovery that the Universe is expanding has produced a revolution in human thought about the Cosmos. American astronomer Edwin Hubble played a major role in this profound discovery, coining the "Hubble constant".
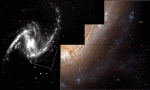 Hubble's Constant And The Expanding Universe (I)
Hubble's Constant And The Expanding Universe (I)
13.05.1996
Our Universe is expanding. Distant galaxies appear to recede from us at ever-increasing speeds. What is the rate of expansion? How long has it been expanding? What will be its ultimate fate? Two groups of astronomers are searching vigorously for answers to these fundamental questions using the Hubble Space Telescope (HST).
|
January February March April May June July August September October |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||