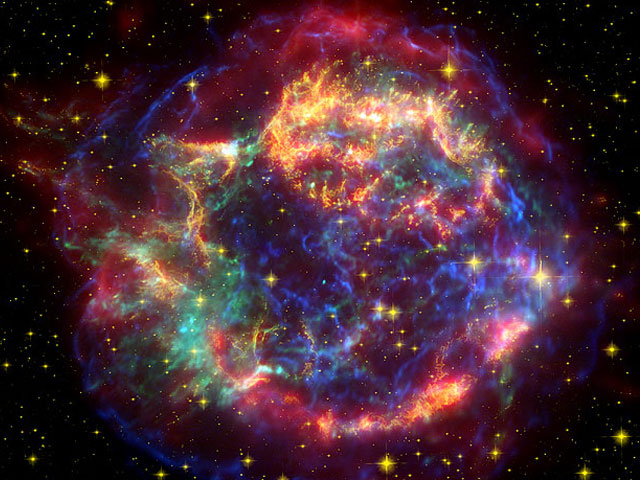
Explanation: Why is the image of Cassiopeia A changing? Two images of the nearby supernova remnant taken a year apart in infrared light appear to show outward motions at tremendous speeds. This was unexpected since the supernova that created the picturesque nebula was seen 325 years ago. The reason is likely light echoes. Light from the supernova heated up distant ambient dust that is just beginning to show its glow. As time goes by, more distant dust lights up, giving the appearance of outward motion. The above image is a composite of X-ray, optical, and infrared light exposures that have been digitally combined. The infrared light image was taken by the orbiting Spitzer Space Telescope and was used in the discovery of the light echo. Cassiopeia A spans about 125 light years and lies 10,000 light years away toward the constellation of Cassiopeia.
Authors & editors:
Robert Nemiroff
(MTU) &
Jerry Bonnell
(USRA)
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings,
and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris.
Specific
rights apply.
A service of:
LHEA at
NASA /
GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Based on Astronomy Picture
Of the Day