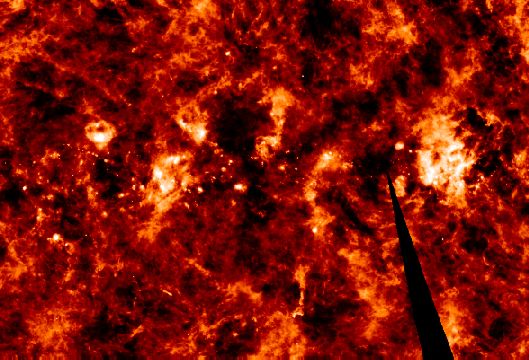
Explanation: Astronomers have recently discovered that looking at dust along the plane of our Milky Way Galaxy is a bit like looking into a frothy glass of beer. The dust between stars in our galaxy is arranged like a foam with bubbles and voids -- apparently churned by shocks and winds generated as stars cycle through their lives. This processed infrared image, based on data from NASA's IRAS satellite, maps the radiation from the edges of galactic dust clouds and reveals the complex distribution. The image covers an area of about 40x60 degrees centered on the galactic plane near the Cygnus region. It shows bright bubble-shaped and arc-like dust clouds around the supernova remnants and starbirth regions embedded in the galactic disk.
Authors & editors:
Robert Nemiroff
(MTU) &
Jerry Bonnell
(USRA)
NASA Web Site Statements, Warnings,
and Disclaimers
NASA Official: Jay Norris.
Specific
rights apply.
A service of:
LHEA at
NASA /
GSFC
& Michigan Tech. U.
Based on Astronomy Picture
Of the Day